imported>Riguz {style="width:400px"} |
小 Riguz移动页面Java GC summary至JVM GC summary,不留重定向 |
||
| (未显示同一用户的13个中间版本) | |||
| 第1行: | 第1行: | ||
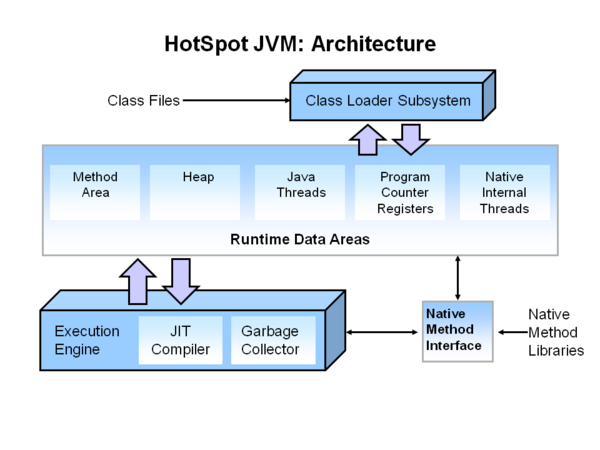
[[File: | [[File:Hotspot-Arch.png|600px|HotSpot JVM architecture]] | ||
= JVM Generations= | = JVM Generations= | ||
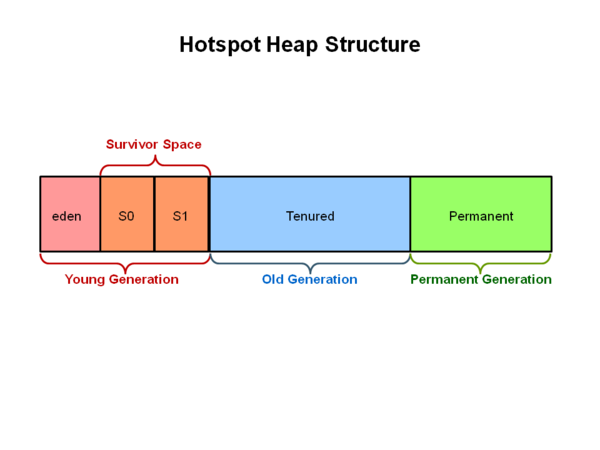
[[File: | [[File:Hotspot-heap.png|600px|Hotspot Heap Structure]] | ||
Java的堆被划分成不同的区域: | Java的堆被划分成不同的区域: | ||
* young | * young generation:存放新创建的对象,当这个区域占满的时候,会触发<span class="article-label">minor GC</span>,这时候存活的对象会被标记年龄,最终会移动到<span class="article-label">old generation</span>。 | ||
* old | * old generation:存放存活的比较久的对象。当<span class="article-label">yound generation</span>存活的对象年龄到达设置的阈值后,就会被移动到这里来。当这个区域满了的时候,会触发<span class="article-label">major GC</span>。 | ||
* permanent | * permanent generation:存放一些JVM运行所需的元数据,例如类的信息等。<span class="article-label">full GC</span>的时候也包括对这个区域的GC。 | ||
其中,<span class="article-label">minor GC</span>和<span class="article-label">major GC</span>都是<span class="article-label">Stop the World</span>的,即当GC触发的时候,所有的程序线程都会停止等待GC完成。通常<span class="article-label">minor GC</span>会比<span class="article-label">major GC</span>快很多,因为<span class="article-label">major GC</span>会遍历所有的存活对象。 | |||
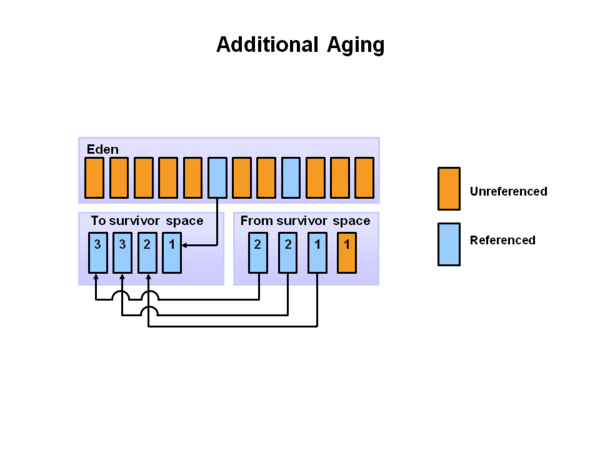
其中,<span class="article-label">yound generation</span> 又被划分成<span class="article-label">Eden space</span>, <span class="article-label">Survivor Space1</span>, <span class="article-label">Survivor Space2</span>,其中<span class="article-label">Eden Space</span>占了绝大部分的空间。当<span class="article-label">Eden space</span>满的时候,GC 会将存活对象移动到其中一个<span class="article-label">Survivor Space</span>中,两个<span class="article-label">Survivor Space</span>是为了避免内存碎片,每次将存活的对象(Eden Space以及上一个Survivor Space)移动到另一个Survivor Space中。 | |||
[[File: | [[File:Hotspot-Aging.png|600px|Mnior GC]] | ||
通过<span class="article-label">Java VisualVM</span>和VisualGC插件可以很直观的看到GC的过程: | |||
[[File:visualVM_GC.png|600px|Visual GC]] | [[File:visualVM_GC.png|600px|Visual GC]] | ||
| 第31行: | 第31行: | ||
= Garbage Collectors= | = Garbage Collectors= | ||
<pre> | |||
Argument Description | Argument Description | ||
--------------- --------------------------------------------------------- | --------------- --------------------------------------------------------- | ||
| 第38行: | 第39行: | ||
-XX:PermSize Sets the starting size of the Permanent Generation. | -XX:PermSize Sets the starting size of the Permanent Generation. | ||
-XX:MaxPermSize Sets the maximum size of the Permanent Generation | -XX:MaxPermSize Sets the maximum size of the Permanent Generation | ||
</pre> | |||
;Serial GC:使用mark-compact算法进行GC,单线程的进行GC,适合单核CPU和在客户端允许的Java程序。 | |||
;Parallel GC(throughput collector):多线程进行GC | |||
;Concurrent Mark Sweep (CMS) Collector: 在程序运行的时候并发的进行GC,以最大限度减少停止时间 | |||
;G1(Garbage-First) Garbage Collector: CMS的替代品 | |||
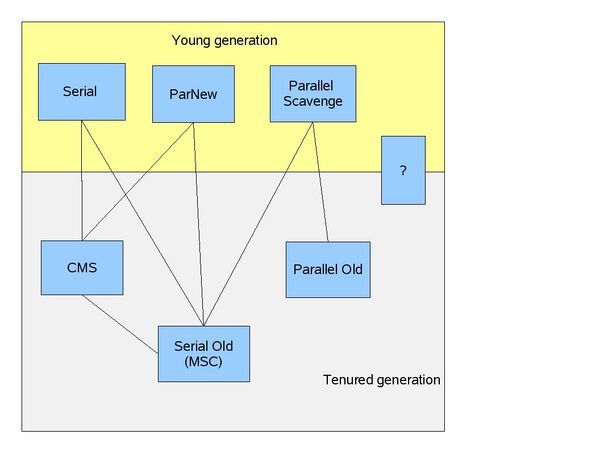
其中存在并行(Parallel)和并发(Concurrent)的区别,并行是指垃圾收集器多个线程同时工作,但此时用户线程依然是停止等待的;而并发是指在用户线程工作的同时,垃圾收集器同时执行。 | 其中存在并行(Parallel)和并发(Concurrent)的区别,并行是指垃圾收集器多个线程同时工作,但此时用户线程依然是停止等待的;而并发是指在用户线程工作的同时,垃圾收集器同时执行。 | ||
[[File: | [[File:JVM-GC-Collectors.jpg|600px|Java collectors]] | ||
<pre> | |||
Garbage Collector Type Algorithm MultiThread | Garbage Collector Type Algorithm MultiThread | ||
----------------- -------------- ------------------------ ---------------------- | ----------------- -------------- ------------------------ ---------------------- | ||
| 第58行: | 第60行: | ||
Parallel Old stop-the-world mark-sweep-compact Yes | Parallel Old stop-the-world mark-sweep-compact Yes | ||
G1 compacting Yes | G1 compacting Yes | ||
</pre> | |||
<pre> | |||
Arguments Result | Arguments Result | ||
------------------------ -------------------------------------------------------- | ------------------------ -------------------------------------------------------- | ||
| 第68行: | 第71行: | ||
-XX:+UseParallelOldGC Parallel Scavenge + Parallel Old | -XX:+UseParallelOldGC Parallel Scavenge + Parallel Old | ||
–XX:+UseG1GC G1 | –XX:+UseG1GC G1 | ||
</pre> | |||
= GC过程= | = GC过程= | ||
== CMS== | == CMS== | ||
CMS 收集器的步骤: | CMS 收集器的步骤: | ||
<pre> | |||
Phase Description | Phase Description | ||
------------------------ ------------------------------------------------------- | ------------------------ ------------------------------------------------------- | ||
| 第80行: | 第84行: | ||
Concurrent Sweep | Concurrent Sweep | ||
Resetting | Resetting | ||
</pre> | |||
G1将Heap划分成一些相同大小的区块,但是没有限制不同代的大小。 | |||
[[File:JVM-GC-G1.png|600px|G1 Heap Allocation]] | |||
= 其他= | |||
当对象被GC(之前)的时候,如果没有执行<span class="article-label">finalize</span>方法,是会执行一次finalize的。如果在finalize方法里面又被强引用了,那么会阻止对象被GC。!! | |||
| 第94行: | 第101行: | ||
* [https://www.oracle.com/webfolder/technetwork/tutorials/obe/java/G1GettingStarted/index.html Getting Started with the G1 Garbage Collector] | * [https://www.oracle.com/webfolder/technetwork/tutorials/obe/java/G1GettingStarted/index.html Getting Started with the G1 Garbage Collector] | ||
[[Category:JVM]] | |||
2023年12月19日 (二) 06:56的最新版本
JVM Generations
Java的堆被划分成不同的区域:
- young generation:存放新创建的对象,当这个区域占满的时候,会触发minor GC,这时候存活的对象会被标记年龄,最终会移动到old generation。
- old generation:存放存活的比较久的对象。当yound generation存活的对象年龄到达设置的阈值后,就会被移动到这里来。当这个区域满了的时候,会触发major GC。
- permanent generation:存放一些JVM运行所需的元数据,例如类的信息等。full GC的时候也包括对这个区域的GC。
其中,minor GC和major GC都是Stop the World的,即当GC触发的时候,所有的程序线程都会停止等待GC完成。通常minor GC会比major GC快很多,因为major GC会遍历所有的存活对象。
其中,yound generation 又被划分成Eden space, Survivor Space1, Survivor Space2,其中Eden Space占了绝大部分的空间。当Eden space满的时候,GC 会将存活对象移动到其中一个Survivor Space中,两个Survivor Space是为了避免内存碎片,每次将存活的对象(Eden Space以及上一个Survivor Space)移动到另一个Survivor Space中。
通过Java VisualVM和VisualGC插件可以很直观的看到GC的过程:
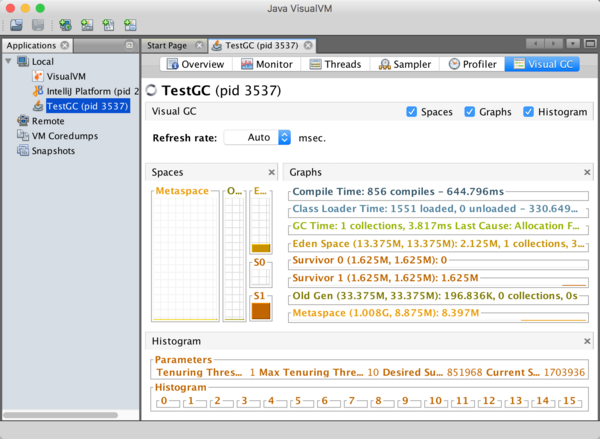
java -Xmx50m \
-XX:-PrintGC \
-XX:+PrintHeapAtGC \
-XX:MaxTenuringThreshold=10 \
-XX:+UseConcMarkSweepGC \
-XX:+UseParNewGC TestGC
Garbage Collectors
Argument Description --------------- --------------------------------------------------------- -Xms Sets the initial heap size for when the JVM starts. -Xmx Sets the maximum heap size. -Xmn Sets the size of the Young Generation. -XX:PermSize Sets the starting size of the Permanent Generation. -XX:MaxPermSize Sets the maximum size of the Permanent Generation
- Serial GC
- 使用mark-compact算法进行GC,单线程的进行GC,适合单核CPU和在客户端允许的Java程序。
- Parallel GC(throughput collector)
- 多线程进行GC
- Concurrent Mark Sweep (CMS) Collector
- 在程序运行的时候并发的进行GC,以最大限度减少停止时间
- G1(Garbage-First) Garbage Collector
- CMS的替代品
其中存在并行(Parallel)和并发(Concurrent)的区别,并行是指垃圾收集器多个线程同时工作,但此时用户线程依然是停止等待的;而并发是指在用户线程工作的同时,垃圾收集器同时执行。
Garbage Collector Type Algorithm MultiThread ----------------- -------------- ------------------------ ---------------------- Serial stop-the-world copying No ParNew stop-the-world copying Yes Parallel Scavenge stop-the-world copying Yes Serial Old stop-the-world mark-sweep-compact No CMS low-pause concurrent-mark-sweep Yes Parallel Old stop-the-world mark-sweep-compact Yes G1 compacting Yes
Arguments Result ------------------------ -------------------------------------------------------- -XX:+UseSerialGC Serial + Serial Old -XX:+UseParNewGC ParNew + Serial Old -XX:+UseConcMarkSweepGC ParNew + CMS + Serial Old^["CMS" is used most of the time to collect the tenured generation. "Serial Old" is used when a concurrent mode failure occurs.] -XX:+UseParallelGC Parallel Scavenge + Serial Old -XX:+UseParallelOldGC Parallel Scavenge + Parallel Old –XX:+UseG1GC G1
GC过程
CMS
CMS 收集器的步骤:
Phase Description ------------------------ ------------------------------------------------------- Initial Mark (Stop-Word) 标记老年代中的对象是否可达(reachable),包括可以从新生代中到达的 Concurrent Marking Remark (Stop-Word) Concurrent Sweep Resetting
G1将Heap划分成一些相同大小的区块,但是没有限制不同代的大小。
其他
当对象被GC(之前)的时候,如果没有执行finalize方法,是会执行一次finalize的。如果在finalize方法里面又被强引用了,那么会阻止对象被GC。!!
References: