| 第26行: | 第26行: | ||
===Safety requirements=== | ===Safety requirements=== | ||
;Validity (or non-triviality):Only a value that has been proposed may be chosen, A process never learns that a value has been chosen unless it actually has been. | |||
;Agreement (or consistency, or safety):Only a single value is chosen, and | |||
;Termination (or liveness): if a value has been chosen, then a process can eventually learn the value. | |||
[[Category:Distributed]] | [[Category:Distributed]] | ||
2021年5月7日 (五) 01:55的版本
Paxos解决的是什么问题
state machine replication
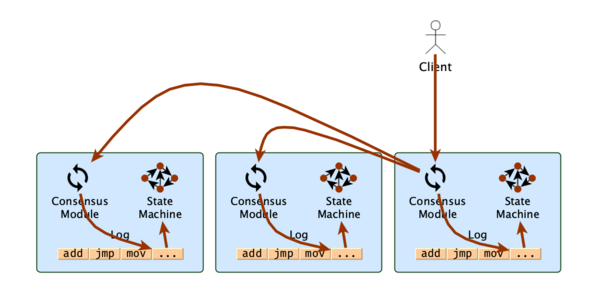
如上所示的系统中,如果客户端要执行某个命令,那么将遵循如下的步骤:
- 发送命令到其中某一个server
- server首先将命令记录到log中,然后将命令发送到其他的服务中;其他server同样将其记录到log中
- 当命令完整的记录到各个server之后,就可以传到state machine去执行了,并将结果返回给客户端
其中,consensus module用来保证log的复制是正确的,也就是paxos要解决的问题。
Paxos算法
The Paxos algorithm, when presented in plain English, is very simple.
推导过程
上述问题可以简化为,有多个服务可以propose value,而共识算法将保证有且仅有一个value会被选中(chosen)。这里面隐含的条件是:
- 如果没有任何value被propose,那么也不应该有任何值被选中
- 值一旦被选中,各个服务应该可以知晓(learn)选中的值
从而可以得出共识算法实现的安全性约束:
Safety requirements
- Validity (or non-triviality)
- Only a value that has been proposed may be chosen, A process never learns that a value has been chosen unless it actually has been.
- Agreement (or consistency, or safety)
- Only a single value is chosen, and
- Termination (or liveness)
- if a value has been chosen, then a process can eventually learn the value.