基本数据类型
Redis的数据类型如下:
- Binary-safe strings
- Strings in Redis are binary safe, meaning they have a known length not determined by any special terminating characters. Thus, you can store anything up to 512 megabytes in one string.
- Lists
- collections of string elements sorted according to the order of insertion. They are basically linked lists.
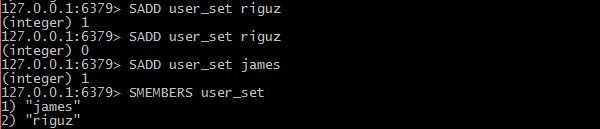
- Sets
- collections of unique, unsorted string elements.
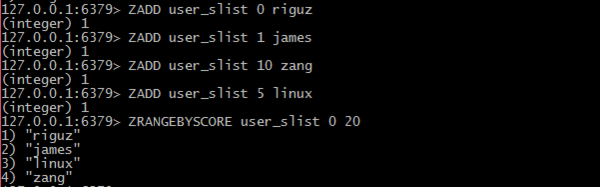
- Sorted sets
- similar to Sets but where every string element is associated to a floating number value, called score. The elements are always taken sorted by their score, so unlike Sets it is possible to retrieve a range of elements
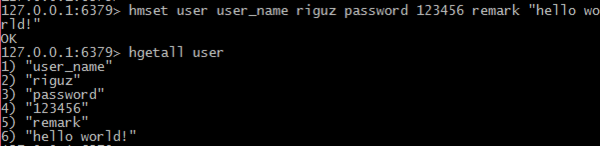
- Hashes
- which are maps composed of fields associated with values. Both the field and the value are strings.
- Bit arrays(bitmaps)
- it is possible, using special commands, to handle String values like an array of bits: you can set and clear individual bits, count all the bits set to 1, find the first set or unset bit, and so forth.
- HyperLogLogs
- this is a probabilistic data structure which is used in order to estimate the cardinality of a set.
- Streams
- append-only collections of map-like entries that provide an abstract log data type.
Binary-safe string
Redis的字符串是字节序列。在Redis中字符串是二进制安全的,这意味着他们有一个已知的长度,是没有任何特殊字符终止决定的,所以可以存储任何东西,最大长度可达512兆。
> set mykey somevalue
OK
> get mykey
"somevalue"
虽然redis中value存储为字符串,但是有一些命令可以按照数字来处理,例如自增:
> set counter 100
OK
> incr counter
(integer) 101
> incr counter
(integer) 102
> incrby counter 50
(integer) 152
批量设置(atomic):
> mset a 10 b 20 c 30
OK
> mget a b c
1) "10"
2) "20"
3) "30"
Lists
Redis Lists are implemented with linked lists because for a database system it is crucial to be able to add elements to a very long list in a very fast way. Another strong advantage, as you'll see in a moment, is that Redis Lists can be taken at constant length in constant time.
List的use cases:
- Remember the latest updates posted by users into a social network.
- Communication between processes, using a consumer-producer pattern where the producer pushes items into a list, and a consumer (usually a worker) consumes those items and executed actions. Redis has special list commands to make this use case both more reliable and efficient.