Distributed:Paxos算法
Paxos解决的是什么问题
state machine replication
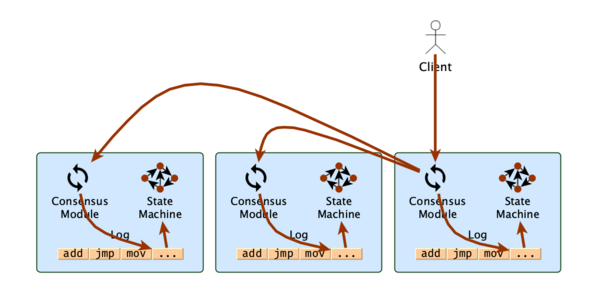
如上所示的系统中,如果客户端要执行某个命令,那么将遵循如下的步骤:
- 发送命令到其中某一个server
- server首先将命令记录到log中,然后将命令发送到其他的服务中;其他server同样将其记录到log中
- 当命令完整的记录到各个server之后,就可以传到state machine去执行了,并将结果返回给客户端
其中,consensus module用来保证log的复制是正确的,也就是paxos要解决的问题。
Paxos算法
The Paxos algorithm, when presented in plain English, is very simple.
共识问题
上述问题可以简化为,有多个服务可以propose value,而共识算法将保证有且仅有一个value会被选中(chosen)。这里面隐含的条件是:
- 如果没有任何value被propose,那么也不应该有任何值被选中
- 值一旦被选中,各个服务应该可以知晓(learn)选中的值
从而可以得出共识算法实现的安全性约束:
Safety requirements
- Validity (or non-triviality)
- Only a value that has been proposed may be chosen, A process never learns that a value has been chosen unless it actually has been.
- Agreement (or consistency, or safety)
- Only a single value is chosen, and
- Termination (or liveness)
- if a value has been chosen, then a process can eventually learn the value.
assumptions
另外,paxos中是不考虑拜占庭问题的,有如下假设成立:
- Agents operate at arbitrary speed, may fail by stopping, and may restart. Since all agents may fail after a value is chosen and then restart, a solution is impossible unless some information can be re- membered by an agent that has failed and restarted.
- Messages can take arbitrarily long to be delivered, can be duplicated, and can be lost, but they are not corrupted.
Choosing a Value
Quorum
Paxos made simple中,从最简单(但不正确)的方式开始,逐步加强约束,最终得到正确的算法。
首先最简单的情况下,只有一个acceptor,然后choose第一个收到的提案。这种办法显然不行,因为一旦这个acceptor出问题了整个系统就没法用了,所以需要有多个acceptor,当系统中有大多数acceptor接受了提案则认为值被choosen。
P1
如果仅有一个proposer提出了一个提案,那么这个提案显然是需要被接受的。因此可推导出约束P1:
P1. An acceptor must accept the first proposal that it receives.