Heap sort
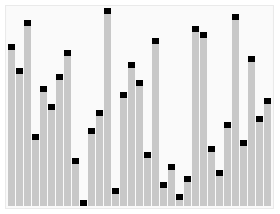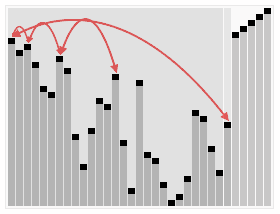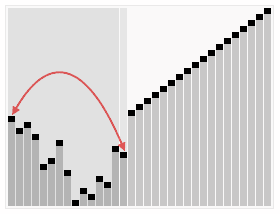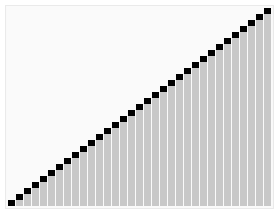
堆排序(Heapsort)是指利用堆这种数据结构所设计的一种排序算法。堆积是一个近似完全二叉树的结构,并同时满足堆积的性质:即子结点的键值或索引总是小于(或者大于)它的父节点。
堆排序的平均时间复杂度为Ο(nlogn) 。
算法描述
- 创建一个堆H[0..n-1]
- 把堆首(最大值)和堆尾互换
- 把堆的尺寸缩小1,并调用shift_down(0),目的是把新的数组顶端数据调整到相应位置
- 重复步骤2,直到堆的尺寸为1
示例代码
C
#define MAX_HEAP_LEN 100
static int heap[MAX_HEAP_LEN];
static int heap_size = 0; // the number of elements in heaps
static void swap(int* a, int* b)
{
int temp = *b;
*b = *a;
*a = temp;
}
static void shift_up(int i)
{
int done = 0;
if( i == 0) return; //node is the root already
while((i!=0)&&(!done))
{
if(heap[i] > heap[(i-1)/2])
{//if the current is larger than the parent, then swap
swap(&heap[i],&heap[(i-1)/2]);
}
else
{// the job is already done.
done =1;
}
i = (i-1)/2;
}
}
static void shift_down(int i)
{
int done = 0;
if (2*i + 1> heap_size) return; // node i is a leaf
while((2*i+1 < heap_size)&&(!done))
{
i =2*i+1; // jump to left child
if ((i+1< heap_size) && (heap[i+1] > heap[i]))
{// find the bigger one of the two children
i++;
}
if (heap[(i-1)/2] < heap[i])
{
swap(&heap[(i-1)/2], &heap[i]);
}
else
{
done = 1;
}
}
}
static void delete(int i)
{
int last = heap[heap_size - 1]; // get the last one;
heap_size--; // shrink the heap
if (i == heap_size) return;
heap[i] = last; // use the last item to overwrite the current
shift_down(i);
}
int delete_max()
{
int ret = heap[0];
delete(0);
return ret;
}
void insert(int new_data)
{
if(heap_size >= MAX_HEAP_LEN) return;
heap_size++;
heap[heap_size - 1] = new_data;
shift_up(heap_size - 1);
}
C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void shift(int d[], int ind, int len){
//置i为要筛选的节点
int i = ind;
//c中保存i节点的左孩子
int c = i * 2 + 1; //+1的目的就是为了解决节点从0开始而他的左孩子一直为0的问题
//未筛选到叶子节点
while(c < len){
//如果要筛选的节点既有左孩子又有右孩子并且左孩子值小于右孩子
//从二者中选出较大的并记录#%
if(c + 1 < len && d[c] < d[c + 1])
c++;
//如果要筛选的节点中的值大于左右孩子的较大者则退出
if(d[i] > d[c]) break;
else{
int t = d[c];
d[c] = d[i];
d[i] = t;
//重置要筛选的节点和要筛选的左孩子
i = c;
c = 2 * i + 1;
}
}
return;
}
void heap_sort(int d[], int n){
//初始化建堆, i从最后一个非叶子节点开始
for(int i = (n - 2) / 2; i >= 0; i--)
shift(d, i, n);
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){
int t = d[0];
d[0] = d[n - j - 1];
d[n - j - 1] = t;
//筛选编号为
shift(d, 0, n - j - 1);
}
}
int main(){
int a[] = {3, 5, 3, 6, 4, 7, 5, 7, 4};
heap_sort(a, sizeof(a) / sizeof(*a));
for(int i = 0; i < sizeof(a) / sizeof(*a); i++){
cout << a[i] << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
Python
def heap_sort(lst):
def sift_down(start, end):
"""最大堆调整"""
root = start
while True:
child = 2 * root + 1
if child > end:
break
if child + 1 <= end and lst[child] < lst[child + 1]:
child += 1
if lst[root] < lst[child]:
lst[root], lst[child] = lst[child], lst[root]
root = child
else:
break
# 创建最大堆
for start in xrange((len(lst) - 2) / 2, -1, -1):
sift_down(start, len(lst) - 1)
# 堆排序
for end in xrange(len(lst) - 1, 0, -1):
lst[0], lst[end] = lst[end], lst[0]
sift_down(0, end - 1)
return lst
def main():
l = [9,2,1,7,6,8,5,3,4]
heap_sort(l)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
